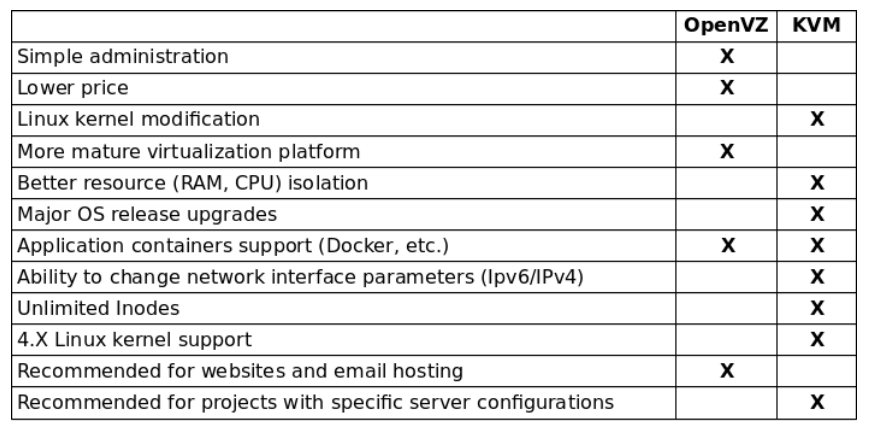
When evaluating Virtual Private Servers (VPS), a common question arises: "Which virtualization method is better, KVM or OpenVZ?" While there are several options to consider, such as Hyper-V, Xen, and VMware, let’s focus on the two prevalent choices available through BuyCheapVPS : KVM and OpenVZ.
OpenVZ
OpenVZ is a container-based virtualization technology for Linux. It operates at the OS level, meaning that multiple containers share the same underlying kernel but act as independent servers. Each container can be rebooted separately and has its own root access, users, IP addresses, memory, processes, files, applications, system libraries, and configuration files. This approach leads to more efficient resource utilization.
Pros: OpenVZ offers good performance with lower resource requirements for the host. End users benefit from easily installed, predefined templates that simplify setup.
Cons: OpenVZ relies on the host’s kernel modules, so if a specific module is missing, you may have no option to add it.
KVM
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) provides full virtualization. With KVM, you can run both Linux and Windows virtual machines on the same hardware. Each virtual machine operates with its own virtualized hardware—kernel, network card, disk, graphics adapter, etc.—allowing it to function completely independently.
Pros: KVM ensures that all applications work as if they were on a dedicated server. It offers flexibility for migrating between virtual machines and dedicated servers, and each VM has its own kernel.
Cons: KVM requires more host resources compared to OpenVZ, which can lead to a slight performance penalty in terms of I/O and CPU usage.
Key Differences Between KVM and OpenVZ